Making Digital Photos Sing
Basic Image Optimization Using Photoshop
Photoshop, in one version or another, is the image-editing application of choice by the majority of photographers. Although it can work miracles with images, the quality and effectiveness of the result is in large part due to what is done initially when an image file is brought into the system. This optimization is often called color correction, and it assumes that the desire is to remove an unwanted color cast or color imbalance. In addition, the information in an image file brought into Photoshop very often may not fully utilize the color space (gamut). Color correction, then, is a process of using the tools provided in Photoshop with the objective of fully utilizing the color space available (gamut) and eliminating any information which detracts from the subject. |
|
A Good Beginning |
|
Photoshop's Color
Correction Tools |
|
Photoshop Elements users should,
if they have not already discovered it, know that Adobe has not included
Curves in that application. So, to adjust an image's overall contrast
in Elements I would suggest using the contrast adjustments available in
the Color Variations tool by Lightening or Darkening highlights, midtones,
and shadows selectively. The Color Variations dialog provides the distinct
advantage of selecting and then making adjustments to the image on the
basis of a side by side before-and-after pair of large thumbnail windows.
After using Color Variations to adjust image contrast to provide good
detail in tones throughout the range of the photo, you will need to use
Levels (again) to be sure the gamut is optimized. |
|
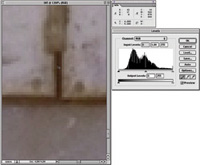
Using Photoshop Levels
To Easily Optimize An Image Using Levels To Set
White/Black And Gray And Remove Color Casts |
|
Setting White, Black,
And Middle Gray Next, using the Navigator,
move the enlarged view to the part of the image which has the darkest
shadows in the picture. Then click on the far left Eyedropper icon button,
and move the mouse cursor to the pixels that look the blackest. Again,
using the numeric RGB values read-out in the Info window, find the one
pixel with the lowest values--note if the values for each RGB channel
are different, and if so, that identifies a color cast. With the darkest,
lowest value pixel identified, click on it and the black point will be
set and the color cast removed. |
|
If there is an area within
a photo image which should be neutral gray, then the middle Eyedropper
icon button can be clicked, and, again, using a magnified view of that
area that should be gray, a pixel can be selected and clicked on to shift
the image values to neutral, thus removing the color cast. Straight Talk About
Using Curves |
|
When To Use Photoshop's
Color Balance Tool |
|
Using Photoshop's
Hue/Saturation Tool |
|
Multiple Selective
Color Adjustments |
- Log in or register to post comments